
We continue to hear more about renewable energy, batteries and microgrids than ever before. Some of this information can be quite technical, so we’ve broken down these types of distributed energy resources to help you navigate the changes in energy sources and uses.
What Are DERs and Why Are They Effective?
A distributed energy resource (DER) is typically referred to as a local energy-generating source, either connected to the utility grid or designed as a stand-alone microgrid. DERs enable a smarter distribution of energy than the traditional power grid in several ways. They offer:
- Improved efficiency: Typically, the utility grid is comprised of centralized power plants creating massive amounts of power and distributing it to end users. Energy has to travel great distances, creating inefficiencies.
- Increased resiliency: It also leads to less resiliency; if the power plant or any part of the distribution system goes down for any reason, end users are without power.
- Cleaner power: DERs decarbonize power with the use of renewable energy as the primary energy source.
Here’s how DERs are used:
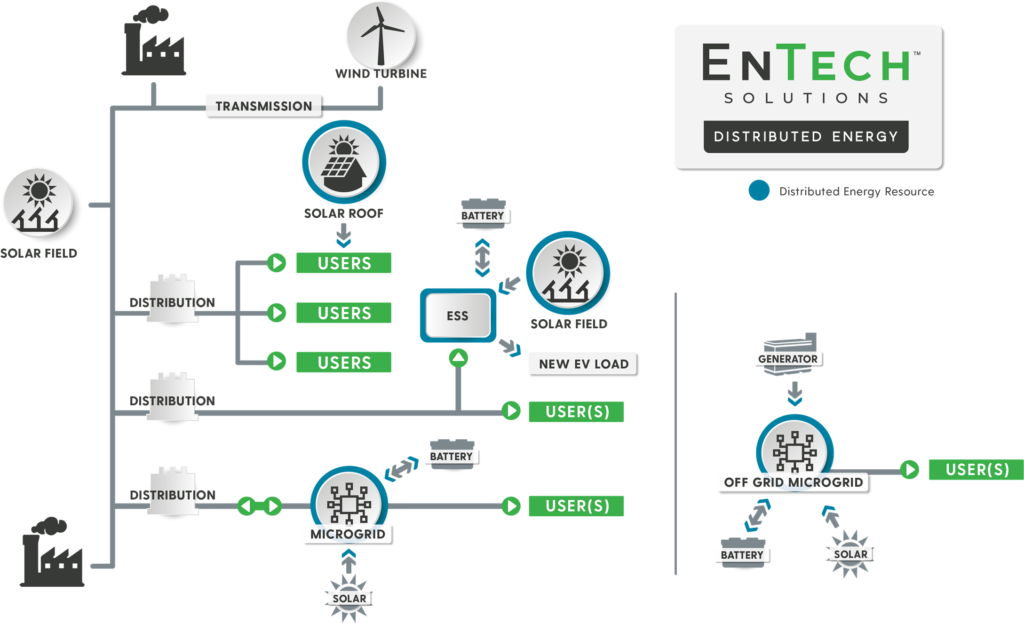
Common Types of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Wind Turbines

You have likely seen these large spinning devices in action, especially in rural areas around the country. They are growing in popularity and can provide energy when the wind blows. Wind turbines turn when wind passes over the blades, which then runs a generator in the head of the turbine and generates power. These turbines are essentially giant generators that run on wind instead of diesel or natural gas.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Panels

Have you ever wondered how a solar panel works? Photons (essentially balls of sunlight) knock loose electrons within the panel. Because electrons “want” to get to the closest positively charged molecule, they are forced to travel through a wire to get to that molecule. This creates electricity, which can be used to power businesses and homes. Prices on solar panels have dropped by 90% over the last 10 years, leading to a boom in popularity.
Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Energy storage systems can come in many forms, from flywheels to large tanks of hydrogen. When we mention ESS, we typically mean lithium-ion batteries. Similar to solar, the popularity of batteries are gaining momentum and the prices are starting to drop as well. Energy storage systems do just as the name implies; they store energy. This energy can be stored mechanically, electrically or chemically when there is more energy produced than needed, and then that same energy is released when it is needed.
The key features of energy storage systems are their response time, efficiency and energy density. The technologies on these systems will only improve as research continues to create better products that enhance those features. Renewable energy has long had critics asking, what happens when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing? Energy storage systems can solve these intermittency issues, making that narrative a thing of the past.
Generators
Generators have been around for a long time. They operate on a wide range of fuels and can vary greatly in size. These dependable devices have a strong track record and can enhance resiliency when combined into a system along with renewable energy and an ESS.
Microgrids
Microgrids are a great way to combine some or all of these resources into one intelligent system. This allows for the solar and/or wind to create power for immediate use, store the excess in an ESS and have a generator pick up any slack. The result is efficient, resilient and sustainable energy for a home or business. Some types of microgrids are completely off-grid (islanded), while others are grid-connected for added resiliency. In some cases, a grid-connected microgrid can provide excess power back to the utility grid for use by others.
At EnTech Solutions, we partner with you on your energy needs to develop a microgrid system that meets your resilience, sustainability and financial goals. Examples of microgrids and solutions can be seen in our project spotlights.
Contact us today to get started on your microgrid project.
Thank you for checking out the EnTech Solutions blog. To stay up to date with technologies, developments and trends in clean energy, please subscribe.
Thank you for checking out the EnTech Solutions blog. To stay up to date with technologies, developments and trends about clean energy, please subscribe.








