Americans are using more natural gas than ever before. In general, it is a clean-burning fuel that can be utilized in a variety of applications.
As overall demand for natural gas increases as a way to offset the carbon emissions from other energy sources, such as coal, it’s important to understand the role renewable natural gas (RNG) plays in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Natural Gas vs. RNG
When comparing natural gas to renewable natural gas (RNG), perhaps the most important aspect to understand is that the chemical composition of these two fuel sources is exactly the same. Due to the identical chemical properties, RNG can be a substitute for fossil fuel natural gas in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
The key differences between the two fuel sources are the feedstock used to produce the fuel and the impact to the environment during the lifecycle of the production.
Traditional Natural Gas and Growing Environmental Concerns
Traditional natural gas is a fossil fuel that typically comes from two sources: drilling deep underground through shale rock–called hydraulic fracking–or as a byproduct of drilling for oil. Neither source is popular among environmentalists because there is a lot of energy expelled to extract that natural gas, so it limits the “clean energy” aspect of the traditional fossil fuel. There is also growing concern over flare gas and stranded gas as bi-products of the hydraulic fracking process.
Renewable Natural Gas as a Cleaner Alternative
Renewable natural gas is created from multiple sources, including agricultural waste, or by capturing the methane gas offloaded by the decomposition at landfills. Depending on the feedstock used to produce the RNG, the carbon intensity of the production process can have significantly lower levels than that of its fossil fuel counterpart. Reducing carbon intensity leads to methane avoidance and an overall reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon intensity values assigned to the RNG can also help petroleum product producers reach sustainability goals and reduce the overall carbon footprint of their operations.
Therefore, it’s not only about what we are creating, but also about what we are not creating. By using waste materials and diverting potential greenhouse gasses, producing RNG is a carbon-negative process.
How is RNG Produced?
As mentioned above, renewable natural gas is generated by capturing harmful gasses emitted from organic waste material, including:
- Wastewater treatment processes
- Agriculture waste, including manure
- Food and beverage waste
- Compost such as garden and lawn clippings
- Landfill gases
As the organic materials break down, they produce biogas, which contains methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and other trace contaminants. This biogas is then cleaned and conditioned to produce RNG.
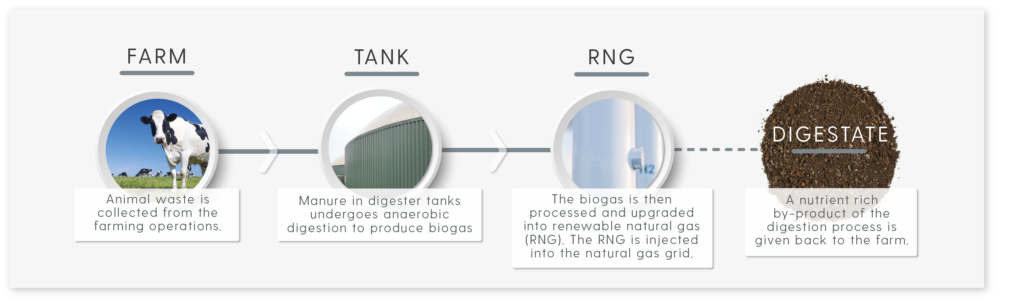
Let’s look at agricultural and dairy waste as an example.
The anaerobic digestion process used to capture methane from dairy cow waste and create RNG celebrates environmental attributes along the entire length of the value chain. In fact, studies show that RNG made from dairy cow manure can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 400% over the life cycle of traditional fuels.
Why is RNG in High Demand?
The increased interest in renewable natural gas is not surprising when you consider all its benefits:
- The abundance of waste materials makes RNG production readily available.
- RNG uses the existing infrastructure and pipelines available throughout the country.
- You can count on RNG day or night in any kind of weather, which makes it an excellent complimentary fuel source in connection with other energy resources.
- Producing and using RNG can be a carbon-negative process, making it a desirable option for companies and communities with the goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
- RNG can be a suitable feedstock for use in the production of green hydrogen and petrochemicals.
- Provides an environmentally cleaner fuel for the transportation industry and helps meet stringent emission standards.
How Can EnTech Solutions Help You Produce RNG?
If your organization is looking at ways to begin RNG production, consider a conversation with the experts at EnTech Solutions about how renewable natural gas might fit into your energy plans. A great example is our successful venture with Northern Biogas to create an active RNG production facility near Madison, Wisconsin.
Other possibilities for partnership might include:
- Capturing methane from your processes. Methane is a common byproduct on farms, from landfills and as part of a variety of industrial processes. We can help you use this waste to create renewable natural gas for a renewable energy source.
- Engineering and constructing renewable natural gas facilities. We can help you build your own RNG production facility.
- Building a microgrid onsite for greater energy resiliency. We can integrate microgrid technology at your facility to ensure operational uptime and to provide a sustainable energy source for the site.
For more information about renewable natural gas as part of your clean energy strategic goals, contact EnTech Solutions at 920-225-6737 or [email protected].
Thank you for checking out the EnTech Solutions blog. To stay up to date with technologies, developments and trends about clean energy, please subscribe.